Quantitative and ultrasensitive detection of brombuterol by a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)-based lateral flow immunochromatographic assay (FLIA) using AgMBA@Au–Ab as an immunoprobe
Abstract
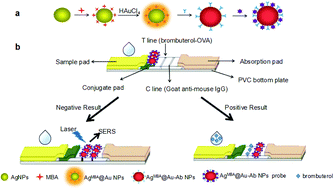
Brombuterol is a new emerging β-adrenergic agonist that has been used as an additive in animal feed to enhance the lean meat-to-fat ratio. Due to its potential harm to consumers, it is urgent to develop sensitive, simple and rapid analytical methods to monitor brombuterol residue. In this study, a competitive lateral flow immunochromatographic assay (FLIA) based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) was developed for ultrasensitive quantitative determination of brombuterol in swine liver, pork and feed samples. Ag@Au core–shell bimetallic nanoparticles with the highest SERS enhancement were synthesized, characterized and used as the substrate for preparation of the immunoprobe AgMBA@Au–Ab, in which the Raman reporter mercaptobenzoic acid (MBA) was embedded between the core–shell layers and monoclonal antibodies against brombuterol were immobilized on the surfaces of nanoparticles. The presence of brombuterol was identified through a color change on testing lines. In addition, quantitative detection of brombuterol was achieved by measuring the characteristic Raman peak intensity of MBA in the immunoprobes captured by the coating antigen. The IC50 and limit of detection (LOD) of the SERS-based FLIA for brombuterol were 45 pg mL−1 and 0.11 pg mL−1, respectively. The recoveries of brombuterol from spiked samples were in the range of 87.27–100.16% with relative standard deviations of 1.29%–6.99% (n = 3). The proposed SERS-based LFIA was proven to be a feasible method for ultrasensitive and rapid detection of brombuterol and might be a platform for sensitive and rapid detection of a broad range of analytes in clinical, environmental and food analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...