Synthesis of CsPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals with acoustically actuated millisecond mixing†
Abstract
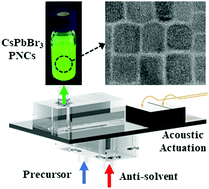
The rapid nucleation and growth dynamics of metal halide perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs) present major challenges in controlling their ensemble evolution and scaling using typical batch syntheses. Continuous flow approaches are an alternative scalable and high-throughput process that can address these limitations by enabling rapid mixing and more precise control of reaction profiles. In this work, we use an acoustically actuated mixer within a continuous microfluidic (MF) platform to study the effect of precursor mixing rate on the synthesis of CsPbBr3 PNCs using the ligand assisted reprecipitation (LARP) approach. It is found that near complete mixing can be achieved at <23 ms timescales under highly efficient acoustic mixing. This enables superior control of the nanocrystal formation stages compared to both non-actuated MF and the standard batch LARP syntheses, which can take more than 2 s to achieve complete mixing with magnetic stirring. Through the study of the temporal evolution of the optical properties in the MF system, it is further found that nanoplatelet formation dominates during early reaction times <200 ms, which subsequently transform into nanocuboids. This complex colloidal evolution of PNCs further validates the need to achieve mixing at the millisecond timescale to afford structurally controlled PNCs with minimal polydispersity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...