Poly(acrylic acid)-mediated synthesis of cerium oxide nanoparticles with variable oxidation states and their effect on regulating the intracellular ROS level†
Abstract
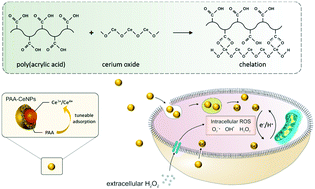
Cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeNPs) possess multiple redox enzyme mimetic activities in scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS) as a potential biomedicine. These enzymatic activities of CeNPs are closely related to their surface oxidation state. Here we have reported a synthetic method to modify CeNPs’ surface oxidation state by changing the conformation of the poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) polymers adsorbed onto the CeNP surface. The synthesized PAA–CeNPs exhibited the same core size, morphology, crystal structure, and colloidal stability, with the only variation being their surface oxidation state (Ce3+ percentage). The modification mechanism can be attributed to the polymers chemisorbed onto the metal oxide surface forming a metal complexation structure. Such adsorption further modified CeNPs’ surface oxidation state in a temperature-dependent manner. The series of PAA–CeNPs exhibited multiple redox enzyme mimetic activities (superoxide dismutase, catalase, peroxidase, and oxidase) directly related to their surface oxidation state. In vitro experiments showed no cytotoxic effect of these PAA–CeNPs on the osteoblastic cell line SAOS-2 at high loadings. Microscopic images confirmed the internalization of PAA–CeNPs in the cells. All tested PAA–CeNPs can reduce the basal and hydrogen peroxide-induced intracellular ROS level in the cells, indicating their effective intracellular ROS scavenging effect. However, we did not observe a positive correlation between the CeNP surface oxidation state and their capacities to reduce the intracellular ROS levels. We propose that CeNPs can maintain a dynamic state of Ce3+/Ce4+ during their catalytic activities, exhibiting a non-linear correlation between the CeNP surface oxidation state and their effect on regulating the intracellular ROS level.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...