Mechanically stable structured porous boron nitride with high volumetric adsorption capacity†
Abstract
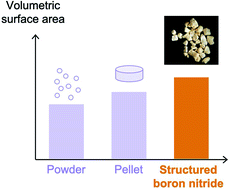
The development of adsorbents into structured and robust forms remains a challenge for emerging porous materials. In the context of porous boron nitride (BN), studies point to a tradeoff between mechanical stability, porosity, density, and adsorption kinetics. Approaches towards shaping and densification of porous BN have been mostly empirical since a detailed understanding of its formation mechanism, and how it impacts mechanical strength and porosity, is lacking. Here, we demonstrate a synthesis method that can directly produce a mechanically robust structured BN from an easily scalable polymeric precursor, which results in the highest volumetric surface area among porous BN samples to date. Structured BN exhibits a high bulk density (ca. 0.3 cm3 g−1), 50% higher than BN powders and over ten times higher than the structured BN aerogel, while maintaining fast sorption kinetics. Structured BN presents good mechanical strength, with hardness of 66.4 ± 4.5 MPa determined via microindentation, i.e. one to two orders of magnitude higher than reported structured aerogels. Using a range of material characterisation techniques, we propose a formation mechanism for structured BN. This formation mechanism reveals that the crosslinked intermediates are responsible for the high mechanical strength of the final material. Our approach produces a form of BN that addresses the limitations of other BN- and non BN-based adsorbents, and facilitates their application in gas separation and storage technologies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...