Oxygen evolution catalysts under proton exchange membrane conditions in a conventional three electrode cell vs. electrolyser device: a comparison study and a 3D-printed electrolyser for academic labs†
Abstract
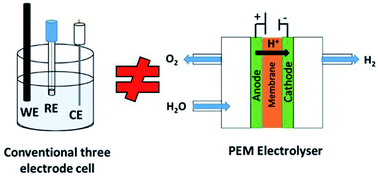
Developing active and stable oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts that can operate in electrolyser environments is of utmost important in order to produce H2 gas for electricity generation. Currently in academia, many of these studies are carried out in conventional three-electrode cell set-ups; however, this configuration may not accurately represent conditions experienced under practical electrolyser conditions. Herein, a range of transition metal oxide (TMO) catalysts are evaluated and compared in a three-electrode cell and in an electrolyser. We show that the same catalyst significantly underperforms in a three-electrode cell. Hence, many OER catalysts in academic labs may have been erroneously omitted from further optimisation processes due to showing ‘poor’ performance in conventional three-electrode cells. Herein, we wish to show this discrepancy experimentally and suggest a solution to scientists wanting to find active OER catalysts by using 3D-printing to inexpensively manufacture electrolyser devices for OER catalyst evaluation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...