Superwetting membranes: from controllable constructions to efficient separations
Abstract
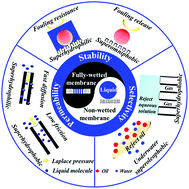
The exploitation of superwetting surfaces including non-wetted (liquid contact angle > 150°) and fully-wetted (liquid contact angle < 10°) surfaces has a long history, and it is still a hot topic from fundamentals to applications in recent years. For membrane separation processes, the superwetting properties of membrane surfaces and pore walls have a great effect on membrane performances. The liquid could rapidly spread onto the fully-wetted membrane surfaces, resulting in a Laplace pressure towards the interior membrane, and thus facilitating mass transfer. Likewise, an air layer between the solid and liquid phases of the non-wetted membrane surfaces could repel the droplet to remove the oil foulant or reduce friction to accelerate liquid transport along the non-wetted membrane pore walls. This review will highlight the superwetting effects on the permeability, selectivity, and stability of membranes. In addition, superwetting membranes can be precisely constructed by regulating the chemical composition and surface topology under the guidance of wetting theories, and the construction methods can be classified into physical and chemical methods based on the major interaction forces during the membrane fabrication processes. Superwetting membranes have been applied for oil–water separation, desalination, carbon dioxide capture, and so on, and the superwetting effects will be analyzed for each application in this review. Moreover, the opportunities and challenges for the future development of the superwetting membranes will be proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...