Network structure of swollen iodine-doped poly(vinyl alcohol) amorphous domain as characterized by low field NMR†
Abstract
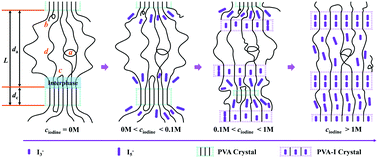
The network structure in the amorphous domain of swollen iodine-doped poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) was systematically investigated by low-field (LF) NMR techniques to reveal the PVA–iodine complex formation mechanism. Three PVA–iodine complexes were obtained under different iodine concentrations (ciodine) of KI/I2 solution: (i) ciodine < 0.1 M: PVA–I3−/I5− complex only exists in the non-crystalline region, (ii) 0.1 M < ciodine < 1 M: formation of PVA–I3− complex I, and (iii) ciodine > 1 M: formation of PVA–I3− complex II. It was found that there is no intermediate-magnitude chain motion of PVA under dyeing conditions to induce the substance exchange, as evidenced by the unchanged second moment M2 (∼1.2 × 104 m s−2) at elevated temperature (<380 K). The introduction of iodine ions can affect the chain mobility of the interphase and mobile regions. With increasing ciodine, the chain dynamics become more restricted, as detected by the faster decay of the T2 relaxometry results, which further accelerates the complexation process. The residual dipolar coupling strength, Dres, obtained by the more quantitative double-quantum (DQ) NMR, increases abruptly at ciodine > 1 M. This suggests more constraints form in the amorphous network for the PVA–I3− complex II system. The constant defects fraction further reveals that the complexation prefers to happen along the tie chains. These results supply a possible formation pathway for the PVA–iodine complexes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...