Mixed lead–tin perovskite films with >7 μs charge carrier lifetimes realized by maltol post-treatment†
Abstract
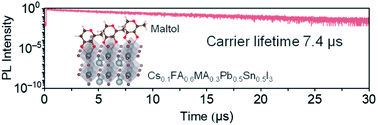
Mixed lead–tin (Pb–Sn) halide perovskites with optimum band gaps near 1.3 eV are promising candidates for next-generation solar cells. However, the performance of solar cells fabricated with Pb–Sn perovskites is restricted by the facile oxidation of Sn(II) to Sn(IV), which induces self-doping. Maltol, a naturally occurring flavor enhancer and strong metal binding agent, was found to effectively suppress Sn(IV) formation and passivate defects in mixed Pb–Sn perovskite films. When used in combination with Sn(IV) scavenging, the maltol surface treatment led to high-quality perovskite films which showed enhanced photoluminescence intensities and charge carrier lifetimes in excess of 7 μs. The scavenging and surface treatments resulted in highly reproducible solar cell devices, with photoconversion efficiencies of up to 21.4% under AM1.5G illumination.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Materials for energy storage and conversion: Chemical Science symposium collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...