A new type of noncovalent surface–π stacking interaction occurring on peroxide-modified titania nanosheets driven by vertical π-state polarization†
Abstract
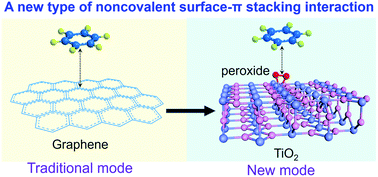
Noncovalent π stacking of aromatic molecules is a universal form of noncovalent interactions normally occurring on planar structures (such as aromatic molecules and graphene) based on sp2-hybridized atoms. Here we reveal a new type of noncovalent surface–π stacking unusually occurring between aromatic groups and peroxide-modified titania (PMT) nanosheets, which can drive versatile aromatic adsorptions. We experimentally explore the underlying electronic-level origin by probing the perturbed changes of unoccupied Ti 3d states with near-edge X-ray absorption fine structures (NEXAFS), and find that aromatic groups can vertically attract π electrons in the surface peroxo-Ti states and increase their delocalization regions. Our discovery updates the concept of noncovalent π-stacking interactions by extending the substrates from carbon-based structures to a transition metal oxide, and presents an approach to exploit the surface chemistry of nanomaterials based on noncovalent interactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...