Heat induction in two-dimensional graphene–Fe3O4 nanohybrids for magnetic hyperthermia applications with artificial neural network modeling
Abstract
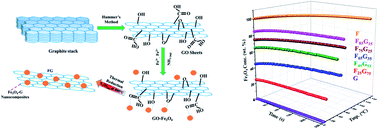
We report the synthesis and characterization of graphene functionalized with iron (Fe3+) oxide (G-Fe3O4) nanohybrids for radio-frequency magnetic hyperthermia application. We adopted the wet chemical procedure, using various contents of Fe3O4 (magnetite) from 0–100% for making two-dimensional graphene–Fe3O4 nanohybrids. The homogeneous dispersal of Fe3O4 nanoparticles decorated on the graphene surface combined with their biocompatibility and high thermal conductivity make them an excellent material for magnetic hyperthermia. The morphological and magnetic properties of the nanohybrids were studied using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM), respectively. The smart magnetic platforms were exposed to an alternating current (AC) magnetic field of 633 kHz and of strength 9.1 mT for studying their hyperthermic performance. The localized antitumor effects were investigated with artificial neural network modeling. A neural net time-series model was developed for the assessment of the best nanohybrid composition to serve the purpose with an accuracy close to 100%. Six Nonlinear Autoregressive with External Input (NARX) models were obtained, one for each of the components. The assessment of the accuracy of the predicted results has been done on the basis of Mean Squared Error (MSE). The highest Mean Squared Error value was obtained for the nanohybrid containing 45% magnetite and 55% graphene (F45G55) in the training phase i.e., 0.44703, which is where the model achieved optimal results after 71 epochs. The F45G55 nanohybrid was found to be the best for hyperthermia applications in low dosage with the highest specific absorption rate (SAR) and mean squared error values.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...