Novel potentiometric sensors for determination of ondansetron hydrochloride in pure and dosage form
Abstract
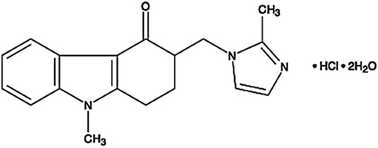
A new and sensitive potentiometric method has been developed and characterized for four novel sensors responsive to ondansetron hydrochloride. The potentiometric sensor method includes advancement of ondansetron hydrochloride sensors using a membrane comprised of molybdophosphoric acid (MPA) and ondansetron as an electro-active material in a polyvinylchloride (PVC) matrix membrane plasticized with di-butyl phthalate (DBPH), ortho-nitrophenyloctyl ether (O-NPOE), di-octyl phthalate (DOPH), or di-butyl phosphate (DBP). The validity of sensors in the present work has been examined, and steady and reproducible responses were obtained over the concentration ranges of 7.3 × 10−5 to 1.0 × 10−2, 6.6 × 10−6 to 1.0 × 10−2, 1.0 × 10−5 to 1.0 × 10−2, and 2.0 × 10−5 to 1.0 × 10−2 M for DBPH-, O-NPOE-, DOPH-, and DBP-ondansetron, respectively. The sensors revealed Nernstian gradients of 59.61 ± 0.50, 57.71 ± 0.23, 53.01 ± 0.14, and 53.20 ± 0.35 mV per decade individually with pH ranges of 2.5–5.5 in DBPH and 3.5–5.0 in O-NPOE electrodes, and 4.0–5.5 for both individual DOPH and DBP plasticized film-based sensors. The time responses for the sensors were 30, 32, 31, and 29 s for DBPH-, O-NPOE-, DOPH-, and DBP-ondansetron, respectively. The developed sensors also exhibited high selectivity towards ondansetron hydrochloride against different interfering species of inorganic particles with long-term stability of approximately 41, 36, 18, and multiple days for the DBPH, O-NPOE, DOPH, and DBP electrodes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...