Improved liquid–liquid extraction by modified magnetic nanoparticles for the detection of eight drugs in human blood by HPLC-MS†
Abstract
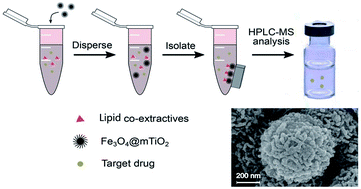
Magnetic nanoparticles modified with porous titanium dioxide were used as clean-up nanospheres for the detection of eight drug poisons in human blood by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The magnetic clean-up nanospheres (Fe3O4@mTiO2) with a mesoporous structure were successfully synthesized and characterized by scanning electron microscopy/energy dispersive spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffractometry, vibrating sample magnetometry, infrared spectroscopy, and Brunauer–Emmett–Teller techniques. Lipid co-extractives, such as phosphatidic acid and fatty acids, which are major interferences in HPLC-MS analysis causing ion suppression in the MS spectra of blood, could be efficiently removed by Fe3O4@mTiO2 based on the Lewis acid–Lewis base interactions. Following the optimization of the quantities of Fe3O4@mTiO2, the method was applied to the determination of eight drugs in spiked blood. The analytical ranges typically extended from 2 to 500 ng mL−1, and the recoveries ranged from 79.5–99.9% at different concentrations of blood. The limits of quantitation for drug poisons were 0.14–1.03 ng mL−1, which makes the method a viable tool for drug poison monitoring in blood.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...