A highly efficient microwave-assisted synthesis of an LED-curable methacrylated gelatin for bio applications†
Abstract
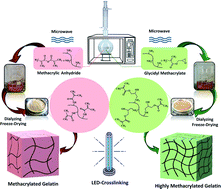
This study deals with the development of an LED-curable methacrylated gelatin (GelMA) synthesis via microwave (MW) irradiation with a reaction and purification time-, energy-, and methacrylation reagent-saving approach. To investigate the efficiency of MW irradiation in GelMA synthesis, characteristics of the GelMAs prepared by using glycidyl methacrylate (GMA) or methacrylic anhydride (MA) via the MW-assisted (MWA) method were compared comprehensively with those synthesized via the conventional heating method. Moreover, MWA reaction conditions were optimized in terms of methacrylation reagent concentrations (C), reaction time (t), and MW power (P). Characterization and assessment of the GelMAs were conducted with 1H NMR, FT-IR, and Raman spectroscopy along with physical-mechanical, thermal, and hydrophilicity analysis. The results demonstrated that the MWA synthesized GMA–GelMA hydrogels were possessed of increased methacrylation degree (MD), gel fraction (GF), tensile strength (TS), elongation at break (EB), glass transition temperature (Tg), and water contact angle (WCA) as well as decreased swelling degree (SD) values in comparison to those of MA–GelMA and GMA–GelMA hydrogels prepared via the MWA and conventional method, respectively. Enhanced properties of the MWA synthesized GMA-hydrogels suggested an effective methacryloyl conjugation leading to a greater amount of covalent crosslinking density justified by the dipolar moment calculations. Optimal GMA C, t, P, and purification time for a highly crosslinked GelMA hydrogel (MD: 96.1%, GF: 98.3%, SD: 10.11%, TS: 6.7 MPa, EB: 175.2%, Tg: 75.34 °C, and WCA: 72.22°) were found to be a 5 times molar excess over the primary amine groups of gelatin, 5 min, 500 W, and 24 h, respectively. Thus, the optimized MW conditions offer a promising green method to prepare GelMAs for bio applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...