Facile construction of a family of supramolecular gels with good levofloxacin hydrochloride loading capacity†
Abstract
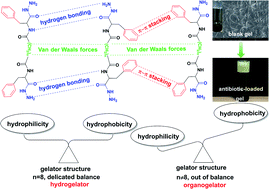
Due to their designability and easy functionalization (such as self-antimicrobial, high antibiotic loading content, injectable, and sustained drug release), low molecular weight gels have attracted significant attention as antimicrobial materials. Herein, a series of biocompatible low molecular weight gelators (LMWGs) were designed and synthesized, using dihydrazides with different alkyl chains, which show excellent gelation ability in PEG200 and PEG400. Among these gelators, a low molecular weight hydrogelator (LMWH) was obtained by introducing an appropriate length of the alkyl chain. The supramolecular gels exhibited good shear thinning behavior, destruction–recovery ability, and excellent antibiotic (levofloxacin hydrochloride) loading capacity (as high as 66.7%). FT-IR and 1H NMR were used for the investigation of the gelation process of gelators. Results suggest that regulating and controlling the balance of the hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts of the gelator structure by introducing different alkyl chain lengths is an effective method for constructing LMWHs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...