Adsorption of azide-functionalized thiol linkers on zinc oxide surfaces†
Abstract
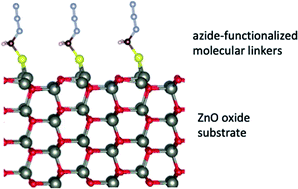
A comprehensive understanding of the interactions between organic molecules and a metal oxide surface is essential for an efficient surface modification and the formation of organic–inorganic hybrids with technological applications ranging from heterogeneous catalysis and biomedical templates up to functional nanoporous matrices. In this work, first-principles calculations supported by experiments are used to provide the microstructural characteristics of (10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) surfaces of zinc oxide single crystals modified by azide terminated hydrocarbons, which graft on the oxide through a thiol group. On the computational side, we evaluate the specific interactions between the surface and the molecules with the chemical formula N3(CH2)nSH, with n = 1, 3, 6, 9. We demonstrate that the molecules chemisorb on the bridge site of ZnO(10
0) surfaces of zinc oxide single crystals modified by azide terminated hydrocarbons, which graft on the oxide through a thiol group. On the computational side, we evaluate the specific interactions between the surface and the molecules with the chemical formula N3(CH2)nSH, with n = 1, 3, 6, 9. We demonstrate that the molecules chemisorb on the bridge site of ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0). Upon adsorption, the N3(CH2)nSH molecules break the neutral (Znδ+–Oδ−) dimers on ZnO(10
0). Upon adsorption, the N3(CH2)nSH molecules break the neutral (Znδ+–Oδ−) dimers on ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) resulting in a structural distortion of the ZnO(10
0) resulting in a structural distortion of the ZnO(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0) substrate. The energy decomposition analysis revealed that such structure distortion favors the adsorption of the molecules on the surface leading to a strong correlation between the surface distortion energy and the interaction energy of the molecule. An azide-terminated thiol with three methylene groups in the hydrocarbon chain N3(CH2)3SH was synthesized, and the assembly of this linker on ZnO surfaces was confirmed through atomic force microscopy. The bonding to the inorganic surface was examined via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Clear signatures of the organic components on the oxide substrates were observed underlying the successful realization of thiol-grafting on the metal oxide. Temperature-dependent and angle-resolved XPS were applied to examine the thermal stability and to determine the thickness of the grafted SAMs, respectively. We discuss the high potential of our hybrid materials in providing further functionalities towards heterocatalysis and medical applications.
0) substrate. The energy decomposition analysis revealed that such structure distortion favors the adsorption of the molecules on the surface leading to a strong correlation between the surface distortion energy and the interaction energy of the molecule. An azide-terminated thiol with three methylene groups in the hydrocarbon chain N3(CH2)3SH was synthesized, and the assembly of this linker on ZnO surfaces was confirmed through atomic force microscopy. The bonding to the inorganic surface was examined via X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). Clear signatures of the organic components on the oxide substrates were observed underlying the successful realization of thiol-grafting on the metal oxide. Temperature-dependent and angle-resolved XPS were applied to examine the thermal stability and to determine the thickness of the grafted SAMs, respectively. We discuss the high potential of our hybrid materials in providing further functionalities towards heterocatalysis and medical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...