Remote dibenzocycloheptyl substitution on a bis(arylimino)pyridyl-iron ethylene polymerization catalyst; enhanced thermal stability and unexpected effects on polymer properties†
Abstract
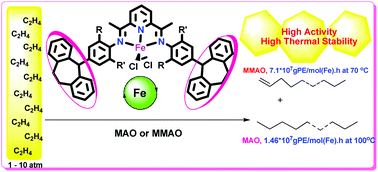
Four examples of para-dibenzocycloheptyl-substituted 2,6-bis(arylimino)pyridyl-iron(II) chloride complexes, [2,6-{(2-R1,4-(C15H13),6-R2C6H2)N![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CMe}2C5H3N]FeCl2 (R1 = R2 = Me Fe1, Et Fe2, iPr Fe3, R1 = Me, R2 = Et Fe4), have been synthesized and characterized by a combination of IR spectroscopy, elemental analysis and single crystal X-ray diffraction. The molecular structures of Fe2 and Fe4 highlight not only their pseudo-square pyramidal geometries but also the variation in configuration of the two remote dibenzo-fused cycloheptyl rings. When activated with MAO or MMAO, Fe1–Fe4 displayed very high activities for ethylene polymerization by operating effectively at 70 °C/10 atm [up to 7.14 × 107 g(PE) mol−1(Fe) h−1] producing high molecular weight linear polyethylene (as high as 98.7 kg mol−1) with a single melting temperature (Tm: >129.7 °C) as well as various levels of vinyl unsaturation. Even at temperatures up to 100 °C, the polymerization activity remained high [up to 1.46 × 107 g(PE) mol−1(Fe) h−1] underlining the good thermal stability of this catalyst class. By contrast at PC2H4 = 1 atm, all polyethylenes produced using Fe1–Fe4 at run temperatures between 20–60 °C exhibited two melting point values with either MAO (Tm1 93.5–116.2 °C, Tm2 124.9–130.0 °C) or MMAO (Tm1 65.1–85.9 °C, Tm2 116.8–122.8 °C) in line with the bimodality of the lower molecular weight polymers. In particular, when MMAO was employed as a co-catalyst, the polyethylene displayed a wax-like composition and displayed a very narrow dispersity (Mw/Mn range: 1.1–1.6).
CMe}2C5H3N]FeCl2 (R1 = R2 = Me Fe1, Et Fe2, iPr Fe3, R1 = Me, R2 = Et Fe4), have been synthesized and characterized by a combination of IR spectroscopy, elemental analysis and single crystal X-ray diffraction. The molecular structures of Fe2 and Fe4 highlight not only their pseudo-square pyramidal geometries but also the variation in configuration of the two remote dibenzo-fused cycloheptyl rings. When activated with MAO or MMAO, Fe1–Fe4 displayed very high activities for ethylene polymerization by operating effectively at 70 °C/10 atm [up to 7.14 × 107 g(PE) mol−1(Fe) h−1] producing high molecular weight linear polyethylene (as high as 98.7 kg mol−1) with a single melting temperature (Tm: >129.7 °C) as well as various levels of vinyl unsaturation. Even at temperatures up to 100 °C, the polymerization activity remained high [up to 1.46 × 107 g(PE) mol−1(Fe) h−1] underlining the good thermal stability of this catalyst class. By contrast at PC2H4 = 1 atm, all polyethylenes produced using Fe1–Fe4 at run temperatures between 20–60 °C exhibited two melting point values with either MAO (Tm1 93.5–116.2 °C, Tm2 124.9–130.0 °C) or MMAO (Tm1 65.1–85.9 °C, Tm2 116.8–122.8 °C) in line with the bimodality of the lower molecular weight polymers. In particular, when MMAO was employed as a co-catalyst, the polyethylene displayed a wax-like composition and displayed a very narrow dispersity (Mw/Mn range: 1.1–1.6).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...