Experimental determination of the curvature-induced intra-wall polarization of inorganic nanotubes†
Abstract
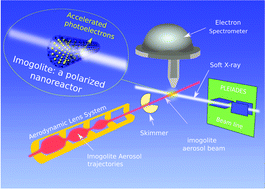
Inspired by a natural nano-mineral known as imogolite, aluminosilicate inorganic nanotubes are appealing systems for photocatalysis. Here, we studied two types of synthetic imogolites: one is completely hydrophilic (IMO-OH), while the other has a hydrophilic exterior and a hydrophobic interior (IMO-CH3), enabling the encapsulation of organic molecules. We combined UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectroscopy of imogolite powders and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy of deposited imogolite films and isolated nanotubes agglomerates to obtain not only the band structure, but also the quantitative intra-wall polarization of both synthetic imogolites for the first time. The potential difference across the imogolite wall was determined to be 0.7 V for IMO-OH and around 0.2 V for IMO-CH3. The high curvature of the nanotubes, together with the thinness of their wall, favors efficient spontaneous charge separation and electron exchange reactions on both the internal and external nanotube surfaces. In addition, the positions of their valence and conduction band edges make them interesting candidates for co-catalysts or doped catalysts for water splitting, among other possible photocatalytic reactions relevant to energy and the environment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...