Adoptive CD8+T-cell grafted with liposomal immunotherapy drugs to counteract the immune suppressive tumor microenvironment and enhance therapy for melanoma †
Abstract
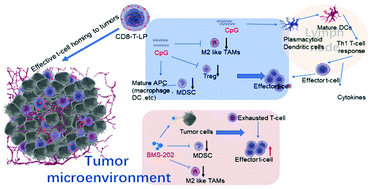
The immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment has become a formidable obstacle to the treatment of tumors using adoptive T cell therapy, in particular solid tumors. For the purposes of addressing this issue, effector OT-1 CD8+T cells conjugated with liposomal immune regulators (CD8-T-LP-CpG/CD8-T-LP-BMS-202) were developed. An anionic liposome formulation was employed to avoid T cell aggregation and prevent unfavorable side-effects. The inclusion of EGCG in the LP-CpG formulation facilitated the formation of compact complexes with poly lysine (PLL) and is thus expected to increase the stability. CD8-T-LP-CpG administered with a median dose of CpG (20 μg per mouse) markedly reduced the frequency of tumor infiltrating polymorphonuclear leukocyte myeloid-derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSCs) (20-folds), M2-like macrophages (8-folds), regulatory T-cells (Treg) (2.7-folds), and consequently increased the frequency of cytotoxic CD8+T cells in tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) (2-folds) and splenic effector memory CD8+T cells (3-folds) relative to the phosphate buffered saline (PBS) control group. Furthermore, the absolute number of tumor infiltrating lymphocyte subtypes altered followed a consistent trend. The difference remained significant compared to the OT-1 CD8+T cells and the drug-loaded liposome combination group. According to in vivo imaging of CD8-T-LP-DiD, we assumed that the improvement in regulation of the tumor microenvironment of LP-CpG/LP-BMS-202 was attributed to the enhanced drug transportation to the tumor site aided by tumor-specific OT-1 CD8+T cells. In addition, CD8-T-LP-BMS-202 administered with a low dose of BMS-202 (1.5 mg per kg body weight) exerted a dramatically improved therapeutic effect by reducing the tumor infiltrating PMN-MDSCs and M2-like macrophages and the corresponding promoted cytotoxic CD8+T cell recruitment in the TILs and effector memory CD8+T cells mediated anti-tumor immunity. In summary, immune therapy drugs backpacked onto adoptive T cell therapy provides a feasible strategy to improve the therapeutic effect and could result in future clinical translation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...