All-purpose nanostrategy based on dose deposition enhancement, cell cycle arrest, DNA damage, and ROS production as prostate cancer radiosensitizer for potential clinical translation†
Abstract
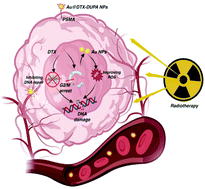
Radiotherapy (RT) is one of the main treatments for men with prostate cancer (PCa). To date, numerous sophisticated nano-formulations as radiosensitizers have been synthesized with inspiring therapeutic effects both in vitro and in vivo; however, almost all the attention has been paid on the enhanced dose deposition effect by secondary electrons of nanomaterials with high atomic numbers (Z); despite this, cell-cycle arrest, DNA damage, and also reactive oxygen species (ROS) production are critical working mechanisms that account for radiosensitization. Herein, an ‘all-purpose’ nanostrategy based on dose deposition enhancement, cell cycle arrest, and ROS production as prostate cancer radiosensitizer for potential clinical translation was proposed. The rather simple structure of docetaxel-loaded Au nanoparticles (NPs) with prostate specific membrane antigen (PSMA) ligand conjugation have been successfully synthesized. Enhanced cellular uptake achieved via the selective internalization of the NPs by PCa cells with positive PSMA expression could guarantee enhanced dose deposition. Moreover, the as-synthesized nanosystem could effectively arrest the cell cycle at G2/M phases, which would reduce the ability of DNA damage repair for more irradiation sensitive of the PCa cells. Moreover, the G2/M phase arrest would further promote cascade retention and the enrichment of NPs within the cells. Furthermore, ROS generation and double strand breaks greatly promoted by NPs under irradiation (IR) could also provide an underlying basis for effective radiosensitizers. In vitro and in vivo investigations confirmed the as-synthesized NPs as an effective nano-radiosensitizer with ideal safety. More importantly, all moieties within the present nanosystem have been approved by FDA for the purpose of PCa treatment, thus making it highly attractive for clinical translation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...