The core composition of DNA block copolymer micelles dictates DNA hybridization properties, nuclease stabilities, and cellular uptake efficiencies†
Abstract
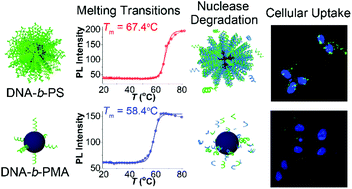
Here, we report how the nature of the hydrophobic core affects the molecular interactions of DNA block copolymer assemblies. Three different amphiphilic DNA block copolymers, DNA-b-polystyrene (DNA-b-PS), DNA-b-poly(2-vinylpyridine) (DNA-b-P2VP), and DNA-b-poly(methyl acrylate) (DNA-b-PMA) were synthesized and assembled into spherical micelles composed of a hydrophobic polymer core and DNA corona. Interestingly, DNA block copolymer micelles having different hydrophobic cores exhibited markedly different molecular and biological interactions. DNA-b-PS exhibited higher melting temperature, sharper melting transition, higher stability to nuclease-catalyzed DNA degradation, and higher cellular uptake efficiency compared to DNA-b-P2VP and DNA-b-PMA. The investigation of the self-assembly behavior revealed a much higher aggregation number and DNA density for DNA-b-PS micelles, which explains the superior properties of DNA-b-PS. These results demonstrate that the type of the hydrophobic core polymer, which has been largely overlooked, has a profound impact on the molecular and biological interactions of the DNA shell.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...