Identification of amyloid beta in small extracellular vesicles via Raman spectroscopy
Abstract
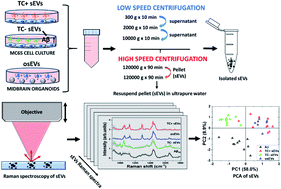
One of the hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis is believed to be the production and deposition of amyloid-beta (Aβ) peptide into extracellular plaques. Existing research indicates that extracellular vesicles (EVs) can carry Aβ associated with AD. However, characterization of the EVs-associated Aβ and its conformational variants has yet to be realized. Raman spectroscopy is a label-free and non-destructive method that is able to assess the biochemical composition of EVs. This study reports for the first time the Raman spectroscopic fingerprint of the Aβ present in the molecular cargo of small extracellular vesicles (sEVs). Raman spectra were measured from sEVs isolated from Alzheimer's disease cell culture model, where secretion of Aβ is regulated by tetracycline promoter, and from midbrain organoids. The averaged spectra of each sEV group showed considerable variation as a reflection of the biochemical content of sEVs. Spectral analysis identified more intense Raman peaks at 1650 cm−1 and 2930 cm−1 attributable to the Aβ peptide incorporated in sEVs produced by the Alzheimer's cell culture model. Subsequent analysis of the spectra by principal component analysis differentiated the sEVs of the Alzheimer's disease cell culture model from the control groups of sEVs. Moreover, the results indicate that Aβ associated with secreted sEVs has a α-helical secondary structure and the size of a monomer or small oligomer. Furthermore, by analyzing the lipid content of sEVs we identified altered fatty acid chain lengths in sEVs that carry Aβ that may affect the fluidity of the EV membrane. Overall, our findings provide evidence supporting the use of Raman spectroscopy for the identification and characterization of sEVs associated with potential biomarkers of neurological disorders such as toxic proteins.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...