Gallium nanoparticles as novel inhibitors of Aβ40 aggregation
Abstract
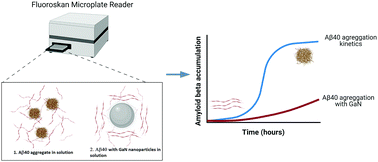
Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been consistently related to the formation of senile amyloid plaques mainly composed of amyloid β (Aβ) peptides. The toxicity of Aβ aggregates has been indicated to be responsible for AD pathology. One scenario to decrease Aβ toxicity is the development of effective inhibitors against Aβ amyloid formation. In this study, we investigate the effect of gallium nitride nanoparticles (GaN NPs) as inhibitors of Aβ40 amyloid formation using a combination of biophysical approaches. Our results show that the lag phase of Aβ40 aggregation kinetics is significantly retarded by GaN NPs in a concentration dependent manner, implying the activity of GaN NPs in interfering with the formation of the crucial nucleus during Aβ aggregation. Our results also show that GaN NPs can reduce the amyloid fibril elongation rate in the course of the aggregation kinetics. It is speculated that the high polarization characteristics of GaN NPs may provoke a strong interaction between the particles and Aβ40 peptide and in this way decrease self-association of the peptide monomers to form amyloids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...