A predictive toolset for the identification of effective lignocellulosic pretreatment solvents: a case study of solvents tailored for lignin extraction†
Abstract
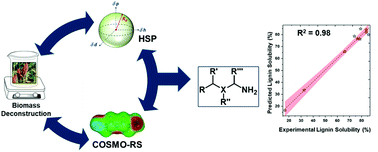
Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass is essential for efficient conversion into biofuels and bioproducts. The present study develops a predictive toolset to computationally identify solvents that can efficiently dissolve lignin and therefore can be used to extract it from lignocellulose during pretreatment, a process known to reduce recalcitrance to enzymatic deconstruction and increase conversion efficiency. Two approaches were taken to examine the potential of eleven organic solvents to solubilize lignin, Hansen solubility parameters (HSP) and activity coefficients and excess enthalpies of solvent/lignin mixtures predicted by COSMO-RS (COnductor like Screening MOdel for Real Solvents). The screening revealed that diethylenetriamine was the most effective solvent, promoting the highest lignin removal (79.2%) and fermentable sugar yields (>72%). Therefore, a COSMO-RS-based predictive model for the lignin removal as a function of number and type of amines was developed. Among the fitted models, the non-linear regression model predicts the lignin solubility more accurately than the linear model. Experimental results demonstrated a >65% lignin removal and >70% of sugar yield from several amine-based solvents tested, which aligned very well with the model's prediction. Finally, to help understand the dissolution mechanism of lignin by these solvents, quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM) and quantum chemical calculations (interaction energies and natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis) was performed and suggest that amines exhibit strong electrostatic interactions and hydrogen bonding strengths with lignin leading to higher lignin removal. Together, these computational tools provide an effective approach for rapidly identifying solvents that are tailored for effective biomass pretreatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...