Flexible on-site halogenation paired with hydrogenation using halide electrolysis†
Abstract
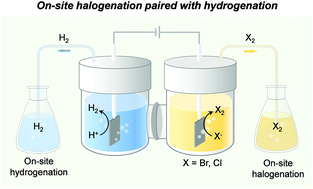
Direct electrochemical halogenation has appeared as an appealing approach in synthesizing organic halides in which inexpensive inorganic halide sources are employed and electrical power is the sole driving force. However, the intrinsic characteristics of direct electrochemical halogenation limit its reaction scope. Herein, we report an on-site halogenation strategy utilizing halogen gas produced from halide electrolysis while the halogenation reaction takes place in a reactor spatially isolated from the electrochemical cell. Such a flexible approach is able to successfully halogenate substrates bearing oxidatively labile functionalities, which are challenging for direct electrochemical halogenation. In addition, low-polar organic solvents, redox-active metal catalysts, and variable temperature conditions, inconvenient for direct electrochemical reactions, could be readily employed for our on-site halogenation. Hence, a wide range of substrates including arenes, heteroarenes, alkenes, alkynes, and ketones all exhibit excellent halogenation yields. Moreover, the simultaneously generated H2 at the cathode during halide electrolysis can also be utilized for on-site hydrogenation. Such a strategy of paired halogenation/hydrogenation maximizes the atom economy and energy efficiency of halide electrolysis. Taking advantage of the on-site production of halogen and H2 gases using portable halide electrolysis but not being suffered from electrolyte separation and restricted reaction conditions, our approach of flexible halogenation coupled with hydrogenation enables green and scalable synthesis of organic halides and value-added products.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2021 Green Chemistry Hot Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...