Strawberry phenolic extracts effectively mitigated metabolic disturbances associated with high-fat ingestion in rats depending on the ellagitannin polymerization degree
Abstract
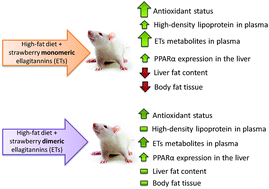
In the present experiment it was hypothesised that dietary strawberry ellagitannin-rich extracts would mitigate negative consequences associated with consumption. Therefore, two extracts rich in dimeric (D-ET) or monomeric (M-ET) ellagitannins (ETs) were added to a standard or high-fat diet fed to rats for four weeks. The D-ET-rich extract contained 82.3% polyphenols, and the M-ET/D-ET ratio was 40 : 60, while the M-ET-rich extract contained 88.0% and 96 : 4, respectively. The experimental feeding with high-fat diets containing extracts resulted in beneficial mitigating effects in the lipid profile, redox status of the rat's liver and blood plasma. According to the accepted hypothesis, the obtained results pointed at increased desired hepatic and plasma modifications when the extract was rich in M-ET, as indicated by favourable changes in the hepatic fat content, GSH and GSSG concentrations and GSH/GSSG ratio as well as blood plasma FRAP, ACL, HDL-cholesterol, and atherogenic coefficient values. These changes were partly connected to the fact that M-ET was more prone vs. D-ET to intestinal microbial conversion into respective metabolites. The urinary daily excretion of ET metabolites and their blood plasma concentrations were higher in rats fed with M-ET vs. D-ET-rich diets. To conclude, the metabolic action of the M-ET-rich extract in the normalization of high-fat-induced disturbances was more pronounced.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...