Bidirectional interaction of nobiletin and gut microbiota in mice fed with a high-fat diet†
Abstract
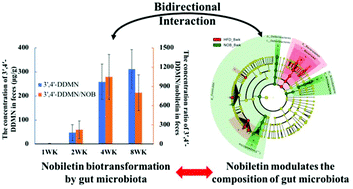
Nobiletin is abundant in citrus peels and demonstrates good anti-obesity bioactivity. However, its anti-obesity mechanisms still remain unclear. This study aims to explore the bidirectional interaction between nobiletin and gut microbiota in mice fed with a high-fat diet. For the colonic bioconversion, more demethylated metabolites with higher biological activity were found in feces than nobiletin in the 48 h excretion study and 8 week consecutive dosing study. Moreover, long-term oral intake of nobiletin would modify the gut microbiota with improved demethylation ability and enhanced production of short chain fatty acids. The comparison of metabolite profiles in mouse liver and feces indicated that gut microbiota might have a higher biotransformation activity on nobiletin than the host. Two bacteria at the genus level, Allobaculum and Roseburia, remained enriched by nobiletin after the 4- and 8-week feedings. They might correlate with the enhanced nobiletin biotransformation and actively contribute to the health benefits of nobiletin in vivo. These results suggested that the bidirectional interaction of nobiletin and gut microbiota played an important role on the anti-obesity effect of nobiletin.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...