The role of the A-cations in the polymorphic stability and optoelectronic properties of lead-free ASnI3 perovskites†
Abstract
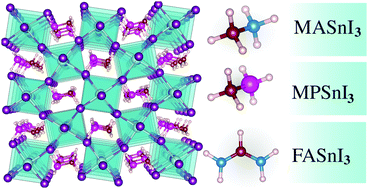
Tin-based ASnI3 perovskites have been considered excellent candidates for lead-free perovskite solar cell applications; however, our atomistic understanding of the role of the A-cations, namely, CH3NH3 (methylammonium, MA), CH3PH3 (methylphosphonium, MP) and CH(NH2)2 (formamidinium, FA), in the physical chemistry properties is far from satisfactory. For the first time, we report a density functional theory investigation of the MPSnI3 perovskite and non-perovskite phases as well as their comparison with the MASnI3 and FASnI3 phases, where we considered the role of the A-cation orientations in the structural stability of the ASnI3 phases. The orthorhombic structure is the most stable studied phase, which agrees with experimentally reported phase-transition trends. In contrast with the cation size and the weak hydrogen bonding interactions, which contribute to structural cohesion between the inorganic framework and A-cation, the dipole–dipole interactions play an important role to drive the structures to the lowest energy configurations. From our analysis, the inorganic framework dominates the optical properties, band structure, and density of states around the band edges. Broader absorption and smaller band gap energies occur for the perovskite structures compared to the low-dimensional hexagonal/pseudo-hexagonal non-perovskites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...