Interfacial activity of modified dextran polysaccharide to produce enzyme-responsive oil-in-water nanoemulsions†
Abstract
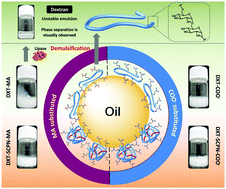
Herein, we report the evaluation of dextran (DXT) derivatives bearing hydrophobic or hydrophilic functional groups as stabilisers of oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions. All investigated modifications conferred interfacial activity to produce stable O/W emulsions, methacrylate(MA)-functionalised DXT being the most promising stabiliser. A minimum amount of MA was required to obtain stable O/W nanoemulsions, which could be degraded in the presence of lipases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...