Development of robust models for rapid classification of microplastic polymer types based on near infrared hyperspectral images†
Abstract
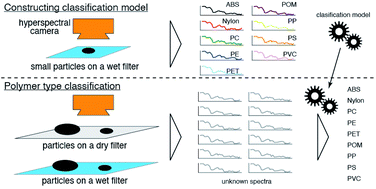
Hyperspectral data in the near infrared range were examined for nine common types of plastic particles of 1 mm and 100–500 μm sizes on dry and wet glass fiber filters. Weaker peak intensities were detected for small particles compared to large particles, and the reflectances were weaker at longer wavelengths when the particles were measured on a wet filter. These phenomena are explainable due to the effect of the correlation between the particle size and the absorption of infrared light by water. We constructed robust classification models that are capable of classifying polymer types, regardless of particle size or filter conditions (wet vs. dry), based on hyperspectral data for small particles measured on wet filters. Using the models, we also successfully classified the polymer type of polystyrene beads covered with microalgae, which simulates the natural conditions of microplastics in the ocean. This study suggests that hyperspectral imaging techniques with appropriate classification models allow the identification of microplastics without the time- and labor-consuming procedures of drying samples and removing biofilms, thus enabling more rapid analyses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...