Ophthalmic sensing technologies for ocular disease diagnostics
Abstract
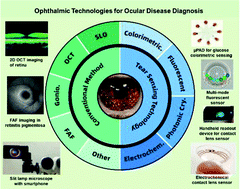
Point-of-care diagnosis and personalized treatments are critical in ocular physiology and disease. Continuous sampling of tear fluid for ocular diagnosis is a need for further exploration. Several techniques have been developed for possible ophthalmological applications, from traditional spectroscopies to wearable sensors. Contact lenses are commonly used devices for vision correction, as well as for other therapeutic and cosmetic purposes. They are increasingly being developed into ocular sensors, being used to sense and monitor biochemical analytes in tear fluid, ocular surface temperature, intraocular pressure, and pH value. These sensors have had success in detecting ocular conditions, optimizing pharmaceutical treatments, and tracking treatment efficacy in point-of-care settings. However, there is a paucity of new and effective instrumentation reported in ophthalmology. Hence, this review will summarize the applied ophthalmic technologies for ocular diagnostics and tear monitoring, including both conventional and biosensing technologies. Besides applications of smart readout devices for continuous monitoring, targeted biomarkers are also discussed for the convenience of diagnosis of various ocular diseases. A further discussion is also provided for future aspects and market requirements related to the commercialization of novel types of contact lens sensors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Review Articles 2021


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...