Plasmonic and label-free real-time quantitative PCR for point-of-care diagnostics†
Abstract
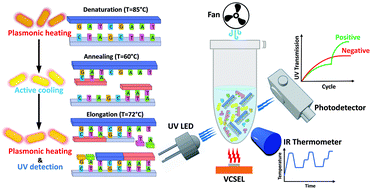
In response to the world's medical community's need for accurate and immediate infectious pathogen detection, many researchers have focused on adapting the standard molecular diagnostic method of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for point-of-care (POC) applications. PCR technology is not without its shortcomings; current platforms can be bulky, slow, and power-intensive. Although there have been some advances in microfluidic PCR devices, a simple-to-operate and fabricate PCR device is still lacking. In the first part of this paper, we introduce a compact plasmonic PCR thermocycler in which fast DNA amplification is derived from efficient photothermal heating of a colloidal reaction mixture containing gold nanorods (AuNRs) using a small-scale vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL). Using this method, we demonstrate 30 cycle-assay time of sub-ten minutes for successful Chlamydia trachomatis DNA amplification in 20 μL total PCR sample volume. In the second part, we report an ultrasensitive real-time amplicon detection strategy which is based on cycle-by-cycle monitoring of 260 nm absorption of the PCR sample. This was accomplished by irradiating the PCR sample using a UV LED and collecting the transmitted optical power with a photodetector. The UV absorption dependency on the nucleotides’ structural degree of freedom gives rise to distinctive features in the shape of UV amplification curves for the determination of PCR results, thus circumventing the need for the complicated design of target-specific probes or intercalating fluorophores. This amplicon quantification method has a high detection sensitivity of one DNA copy. This is the first demonstration of a compact plasmonic thermocycler combined with a real-time fluorophore-free quantitative amplicon detection system. The small footprint of our PCR device stems from hardware miniaturization, while abundant sample volume facilitates highly sensitive detection and fluid handling required for in-field sample analysis, thereby making it an excellent candidate for POC molecular diagnostics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...