Efficient photocatalytic nitrogen fixation under ambient conditions enabled by the heterojunctions of n-type Bi2MoO6 and oxygen-vacancy-rich p-type BiOBr
Abstract
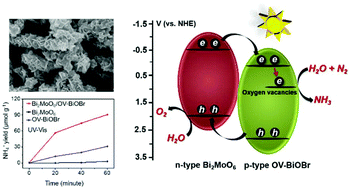
N2 fixation is one of the most important chemical reactions in the ecosystem of our planet. However, the industrial Haber–Bosch ammonia synthesis process is restricted by harsh reaction conditions (350–550 °C, 150–350 atm) and undesirable environmental effects (a large amount of CO2 emission). Photocatalytic N2 fixation is promising for achieving sustainable ammonia synthesis under ambient conditions with lower energy input and less environmental issues. However, the known photocatalysts for N2 reduction under mild conditions still face the great challenge of very low energy conversion efficiency. Herein, we report a facile solution-phase method to prepare the heterojunctions based on n-type Bi2MoO6 nanorods and oxygen-vacancy-rich p-type BiOBr nanosheets (Bi2MoO6/OV-BiOBr). Originating from the formation of p–n junctions and suitable bandgap configuration, the Bi2MoO6/OV-BiOBr heterojunctions exhibit effective light utilization and photogenerated electron–hole separation properties. Moreover, it is confirmed that the oxygen vacancies on BiOBr nanosheets are propitious to the adsorption and activation of N2 molecules. Benefiting from these merits, the Bi2MoO6/OV-BiOBr heterojunctions exhibit improved photocatalytic performance for N2 conversion to ammonia without any noble metal co-catalysts and sacrificial reagents under ambient conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...