Bismuth activated high thermal stability blue-emitting phosphor Na2Y2B2O7:Bi used for near-UV white-light LEDs
Abstract
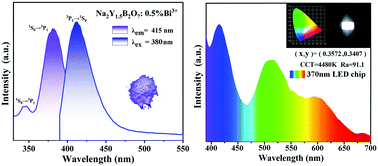
A blue emitting phosphor Na2Y2B2O7:Bi3+ was synthesized by a solid state reaction method. The structure characteristics, concentration, temperature-dependent luminescence and light emitting diode (LED) device performance were systematically studied. Adjustable photoluminescence (PL) from blue to green under different excitation wavelengths from 320 to 390 nm was observed, which is attributed to the complex energy transfer between multiple Bi3+ centres. Moreover, strong absorption in the near ultraviolet region (350–400 nm) was observed in Na2Y2B2O7:Bi3+, which is desirable for LEDs excited by near ultraviolet chips. In addition, a thermal quenching experiment was carried out and the calculated activation energy was 0.28 eV, indicating that this new Na2Y2B2O7:Bi3+ phosphor has good thermal stability. Finally, we explored the application of the Na2Y2B2O7:Bi3+ phosphor by encapsulating LED devices. The device Commission of Illumination (CIE) coordinates are (0.3572, 0.3407), and a high color rendering index (CRI) of 91.1 and a low corresponding color temperature (CCT) of 4480 K under 60 mA current were recorded. These characteristics show that this phosphor can be used to prepare white LED devices excited by near ultraviolet chips.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...