Selectivity of Mn2+ ion occupancy and energy transfer of Ce3+ → Mn2+ ions in garnet solid solution
Abstract
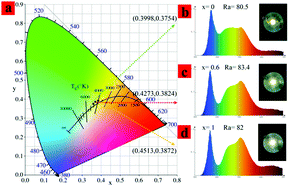
As a luminous center, Mn2+ has the advantages of high efficiency, safety, and low cost, and has been widely used to improve the color rendering index of garnet structured phosphors. Although the position of Mn2+ in garnet structures and its corresponding spectrum have been widely discussed, there is no convincing conclusion. In this paper, the selectivity of Mn2+ ion occupancy in the Y3Al5O12:0.1Ce3+,yMn2+ (y = 0–0.22) garnet structure and their corresponding emission spectra were determined. At low substitution density, Mn2+ ions (y = 0–0.007) easily replace Al3+ ions in the octahedron and emit 590 nm red light under 450 nm blue light excitation, which were determined by calculating the formation energy of the (Mn/Al) and (Mn/Y) local coordination and powder XRD analysis. Upon increasing the Mn2+ concentration from 0.007 to 0.22, the emission light with a peak at 750 nm gradually appears. Meanwhile, the effect of Y3+ ions on the energy transfer of Ce3+ → Mn2+ in (Lu1−xYx)3Al4.8Si0.2O12:0.1Ce3+,0.2Mn2+ (x = 0–1) is achieved through the reduction of the distance between Ce3+ and Mn2+ ions in the dodecahedron. The above work provides support for the correct understanding of the luminescence behavior of Mn2+, and the influence of the microstructure on the energy transfer of Ce3+ → Mn2+ ions. Finally, high color rendering index (83.4) wLEDs were fabricated by the Lu1.2Y1.8Al4.8Si0.2O12:0.1Ce3+,0.2Mn2+ phosphor and the blue chip under 120 mA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...