Self-doped tungsten oxide films induced by in situ carbothermal reduction for high performance electrochromic devices
Abstract
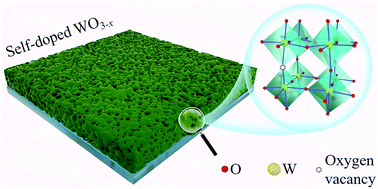
As a promising electrochromic material, tungsten oxide is of great value for applications in smart windows and energy saving displays. Fabricating high performance tungsten oxide by the cost-effective way is immensely in demand for promoting the large-scale application. Herein, we demonstrate a green and economic route in developing self-doped tungsten oxide (WO3−x) films. Through the precursor design and carbonization process, amorphous carbon can be obtained and used as an in situ reducing agent. Then, oxygen vacancies and nanopores were generated in WO3−x films by carbothermal reduction during annealing. The self-doping WO3−x film exhibits a remarkable optical modulation (∼70% at 680 nm) in both visible and near infrared bands. The electrochromic switching behavior of the WO3−x film shows a fast response speed (7 s for coloring and 15 s for bleaching), a high coloration efficiency up to 62 cm2 C−1 and a good cycling stability. The enhanced electrochromic properties are attributed to the large specific surface area and oxygen vacancies which facilitate the ion insertion and extraction at the interface. This work offers a highly active electrochromic material as well as an ingenious synthesis strategy for numerous oxygen deficient functional oxides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...