A key stacking factor for the effective formation of pyrene excimer in crystals: degree of π–π overlap†
Abstract
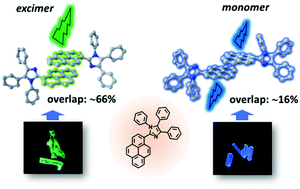
In order to facilitate pyrene (PY) excimer formation in solids, several imidazole-containing PY derivatives were designed and synthesized. Among them, a new compound 1,4,5-triphenyl-2-(pyren-1-yl)-4,5-dihydro-1H-imidazole (IM-PY) was achieved with two crystalline polymorphs (crystal-G and crystal-B), both of which presented PY dimer stacking. One crystal showed green PY excimer emission while the other one exhibited blue monomer emission, despite their similar π–π stacking of PY dimers. Both experimental and theoretical investigations revealed the nature of this distinct emission: the dimer in crystal-B had a smaller overlap area of π–π stacking than that in crystal-G, which substantially hindered PY excimer formation in crystal-B. Through the analysis of PY-based excimer from a series of samples, the π–π overlap area of PY dimer plays a more crucial role in the formation of an excimer than interplanar π–π distance in crystals. This work not only reveals a key structural factor on PY excimer formation in solids, but also provides us with a better understanding of the structure–property relationship between the PY dimer structure and fluorescence property.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...