Enhanced stability and performance of light-emitting diodes based on in situ fabricated FAPbBr3 nanocrystals via ligand compensation with n-octylphosphonic acid†
Abstract
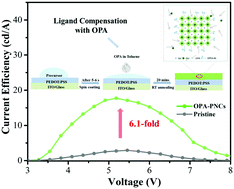
Perovskite-based light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs) are arousing great interest as promising technology for next-generation displays due to their narrow emission linewidth, tunable emission wavelength, and high photoluminescence quantum yield. Due to the superiorities of the simple fabricating process and high efficiency, the in situ preparation of PeLEDs has attracted more attention. However, numerous defects are induced due to the ligand loss in the in situ fabrication of the perovskite film, which restricts the performance improvement of PeLEDs to a larger extent. Here, we introduce a dual ligand 2,2-diphenylethylamine bromide (DPEA-Br) in precursor solution and n-octylphosphonic acid (OPA) in antisolvent for in situ fabricating FAPbBr3 perovskite nanocrystals (PNCs). As a result, the OPA–FAPbBr3 PNC films demonstrate a higher crystallinity, a longer radiative lifetime, and an improved environmental stability, due to the synergistic effect of compensating ligands and passivating defects of OPA. Finally, we obtain a significantly enhanced device efficiency of a maximum luminance of 3273 cd m−2 and a current efficiency of 17.7 cd A−1, which are 12.5 times and 6.1 times higher than those of the control device, respectively. The ligand compensation method with OPA proposed in this work can provide a robust platform for achieving high-quality PNC films and highly efficient PeLEDs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...