Phase control for quasi-2D blue emitters by spacer cation engineering†
Abstract
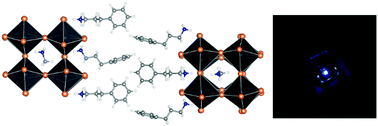
The effect of alkylammonium tail length in phenyl-alkyl spacer cations in quasi-2D Ruddlesden–Popper perovskites on the phase distribution in low n films (n = 2 stoichiometry) is investigated. An increase in alkyl chain length suppresses the formation of the n = 1 phase (and consequently higher n phases), which is attributed to the change in the packing arrangement of spacer cations from parallel (one and two carbon atom alkyl chains) to non-parallel (3 carbon atom alkyl chains). A single blue emission peak corresponding to the n = 3 phase (466 nm) and n = 2 phase (436 nm) is obtained in the PL spectra of phenylpropylammonium quasi-2D perovskites with methylammonium (MA) and formamidinium (FA) cations, respectively. The same trends in phase distribution, namely a reduction in the proportion of the n = 1 phase with increasing alkyl chain length, are observed for both MA- and FA-based perovskites. However, FA-based samples exhibited higher crystallinity but worsened morphology (more pinholes) and less efficient funneling compared to MA-based samples. Consequently, efficient sky-blue LEDs with the highest EQE of 3.35% are obtained for PPA2MAPb2Br7 perovskite.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...