A novel precursor towards buffer layer materials: the first solution based CVD of zinc oxysulfide†
Abstract
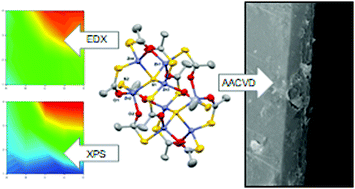
We report the first solution based deposition of zinc oxysulfide, Zn(O,S), thin films via aerosol-assisted chemical vapour deposition (AACVD) facilitated by the use of a specifically designed precursor: [Zn8(SOCCH3)12S2] (1). This buffer layer material, synthesised from the dual source AACVD reaction of 1 with ZnEt2 and MeOH was analysed via X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Hall effect measurements and UV/vis spectroscopy. The film was highly transparent (>90%), conductive (ρ = 0.02998 Ω cm) and had a high charge carrier concentration (1.36 × 1019 cm−3), making it a good contendor as a buffer layer in thin film photovoltaics. In an additional study, large area films were deposited and mapped to correlate compositional variation to optoelectronic properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...