Magnetothermal microfluidic-directed synthesis of quantum dots†
Abstract
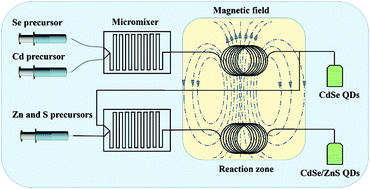
Quantum dots (QDs) have gained extensive attention owing to their outstanding photoelectric properties. However, the fast and continuous synthesis of QDs remains a challenge. Herein, for the first time, we develop a magnetothermal microfluidic technique (MMT) to rapidly synthesize CdSe and CdSe@ZnS QDs with higher optical performance and continuous production. The as-prepared CdSe@ZnS QDs exhibit relatively high photoluminescence quantum yields (PL QYs) (∼70%). Meanwhile, by manipulating the fluid rate and reaction temperature of the MMT, the emission wavelengths can be tuned in the visible region from 515 to 625 nm. Furthermore, the red emissive CdSe@ZnS QDs are used as fluorescent conversion materials in a backlight display, which shows a wide color gamut around 112%. Our purpose is to highlight a new powerful platform of the MMT for rapid, accurate, and continuous fabrication of photoluminescent nanomaterials, which will guide the substantial progress of backlight displays and light emitting diodes (LEDs).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...