Substituent steric effect boosting phosphorescence efficiency of PtCu2 complexes†
Abstract
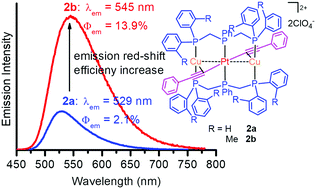
We describe herein a viable approach to enhance phosphorescence efficiency in PtCu2 complexes with aromatic acetylides by the use of bis(di-2-tolylphosphinomethyl)phenylphosphine (dTolmp) in place of bis(diphenylphosphinomethyl)-phenylphosphine (dpmp) as a supporting ligand. Relative to dpmp-supported PtCu2 complexes, dTolmp-supported complexes having the same acetylide ligands show not only a 16–36 nm red-shift of the emission peaks, but also a dramatic phosphorescence enhancement. The phosphorescence quantum yields of dTolmp-supported PtCu2 complexes are boosted to 6.6 and 11.6 times as high as those of the dpmp-supported ones in CH2Cl2 solutions and the solid state, respectively. From dpmp to dTolmp, introducing sterically hindered 2-methyl groups to phenyl rings not only improves the π-conjugation character of PtCu2 complexes, but also effectively inhibits the deactivation process of the triplet excited state through non-radiative relaxation. The phosphorescence properties were systematically modulated in a wide spectral range from 502 to 672 nm by introducing electron-donating or electron-withdrawing substituents into aromatic acetylides.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...