Smart sensing of Cu2+ in living cells by water-soluble and nontoxic Tb3+/Eu3+-induced aggregates of polysaccharides through fluorescence imaging†
Abstract
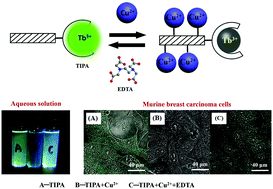
The in vivo trace content of some transition-metal ions is important for biological systems and an inappropriate content may cause diseases. With the purpose of developing an efficient sensing system for Cu2+, this work demonstrates the excellent sensing property of Tb3+/Eu3+-induced polysaccharide aggregates. Photophysical measurements indicate that at a Cu2+ concentration of 20 μM, the fluorescence of Tb3+-induced polysaccharide aggregates (TIPAs) or Eu3+-induced polysaccharide aggregates (EIPAs) can be quenched rapidly and sensitively. Addition of EDTA to chelate Cu2+ restores the fluorescence, indicating that the fluorescence quenching in the presence of Cu2+ is reversible. Initial cytotoxicity experiments with mammalian cells show that the luminescent lanthanide complexes are cytotoxic, but complexing the lanthanides to polysaccharides renders them cytocompatible. These new complexes integrate the advantages of superior lanthanide fluorescence, compatibility with aqueous systems, and cytocompatibility. The microparticle formulation EIPA can be used for applications that require the complexes to be removed from the sample (e.g. by centrifugation), whereas the nanoparticle formulation TIPA is suitable for cell labeling applications with excellent water-solubility, biocompatibility, non-cell toxicity, and cell imaging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...