Flexible TPU strain sensors with tunable sensitivity and stretchability by coupling AgNWs with rGO†
Abstract
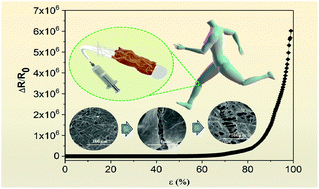
Wearable strain sensors are a compelling need for health monitoring while designing facile and flexible strain sensors with both super-high sensitivity and a wide strain range in an environment-friendly and scalable way remains challenging. Besides, the mechanism underlying these sensors is still insufficiently studied. Here, we propose a handy method to fabricate flexible strain sensors based on an electrospun thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) mat by coupling silver nanowires (AgNWs) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO). The TPU-based strain sensors with AgNWs and rGO alone exhibited high strain sensitivity and a broad working range, respectively, due to the morphological differences between the two types of nanomaterials. In contrast, the rGO/AgNWs/TPU sensor showed a synergistic effect on strain sensitivity and sensing range because of the interaction between the AgNWs and rGO, as well as the coupling effect arising from their assembly. For instance, the sensors with hybrid nanomaterials had ultrahigh sensitivity (gauge factor, GF ≈ 4.4 × 107) and a wider detection range in comparison with the counterpart strain sensors with AgNWs/TPU and rGO/TPU (both GFs in the range of hundreds). Besides, the sensors showed reliable responses to various frequencies and strains, as well as long-term stretching (1000 cycles). These strain sensors were applied to monitor human body motions, such as joint motion and muscle movement, which revealed their potential in healthcare and human-machine interfacing applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...