Ultrafine gold nanoparticle embedded poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride)–graphene oxide hydrogels for voltammetric determination of an antimicrobial drug (metronidazole)†
Abstract
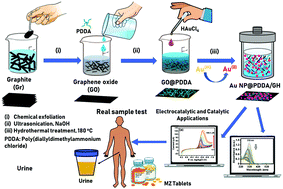
In this work, gold nanoparticle (Au NP) decorated poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) (PDDA) functionalized graphene hydrogel (Au NP@PDDA/GH) nanocomposites were fabricated. The resulting materials were characterized by a variety of analytical and spectroscopic techniques. Electrochemical performances of the prepared composites were examined by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), cyclic voltammetry (CV), and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV). The Au NPs were decorated uniformly and densely on the GO@PDDA composite material based on the electrostatic attraction and this new hierarchical nanostructure can provide a more favourable microenvironment for electron transfer. Under the optimized conditions, the Au NP@PDDA/GH nanocomposite was used as a novel sensing probe for metronidazole (MZ) which was found to have the concentration range of 0.4–656.4 μM with a correlation coefficient (0.999, limit of detection (LOD) based on (LOD = 3k/∂) of 0.097 μM), and a sensitivity of 4.286 μA μM−1. With satisfactory selectivity, reproducibility, and stability, the nanostructure we proposed offered an alternative for electrode fabrication and MZ sensing. Au NP@PDDA/GH was also applied to the reduction of MZ and pharmacy tablets by NaBH4 under ambient conditions. Thus, Au NP@PDDA/GH application provides simplicity, reliability, durability, and low cost benefits.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...