Significant influence of the benzothiophene ring substitution position on the photovoltaic performance of benzodithiophene-based donor polymers†
Abstract
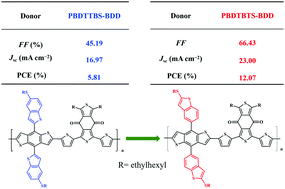
In order to investigate the effects of the substitution position on the photovoltaic performance of donor polymers, two benzothiophene ring substituted benzo(1,2-b:4,5-b′)dithiophene (BDT)-based conjugated polymers (PBDTBTs-BDD and PBDTTBs-BDD) are designed and synthesized. The variation in the substitution position has small influences on the photophysical properties but has a great effect on the intramolecular π–π stack structure, charge transport and photovoltaic properties. PBDTBTs-BDD (with the 6-position of the benzothiophene substituent) exhibited a smaller π–π stacking distance of 3.67 Å compared to 4.11 Å seen for PBDTTBs-BDD (with the 2-position of the benzothiophene substituent). And the charge mobilities of PBDTBTs-BDD-based devices are higher and more balanced than those of PBDTTBs-BDD-based devices, which are highly beneficial for reducing recombination of free carriers and then lead to a higher short-circuit current density (JSC) and fill factor (FF) of devices. With ITIC or Y6 as non-fullerene acceptors, PBDTBTs-BDD-based devices exhibit power conversion efficiencies (PCE) of 7.76% and 12.07%, respectively, which are higher than those of PBDTTBs-BDD-based devices (5.04% and 5.81%). This work demonstrates that the photovoltaic properties of donor polymers can be highly tunable through slight modifications of their side chain structures.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...