Nanostructured copper sulfide thin film via a spatial successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction process showing significant surface-enhanced infrared absorption of CO2†
Abstract
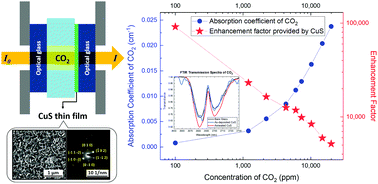
The infrared (IR) gas sensing technique is excellent for CO2 gas detection systems that require high accuracy and safety standard; however, there is a significant barrier to its application due to its high cost and difficulty in miniaturization. CO2 sensors that are functional within near- or short-wavelength IR have the potential to reduce this barrier. In this work, a highly sensitive plasmonic material based on nanostructured covellite copper sulfide (CuS), which exhibits desired localized surface plasmon resonance for surface-enhanced IR absorption (SEIRA) throughout near- and mid-IR ranges, was investigated. We prepared CuS thin films facilely in an additive manner based on a spatial successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction process at room temperature. The resulting CuS thin film possesses a structure consisting of hexagonal nanoflakes, and demonstrates significant SEIRA for 100 ppm CO2 with an enhancement factor of 104.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...