Synthesis of InP branched nanostructures by controlling the intermediate nanoclusters†
Abstract
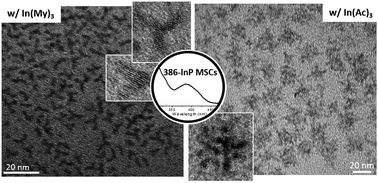
Magic sized clusters (MSCs) are thermodynamically stable intermediate nanoclusters often captured during the growth of semiconductor nanoparticles (NPs). To investigate the role of MSCs in the nucleation and growth into InP NPs and to find new ways to control the InP NP growth pathways, a type of InP MSC (386-MSCs) was used as a precursor to InP NPs. Several heat-up syntheses using the InP 386-MSCs were performed with varying reaction conditions and amounts of additives. Upon heating, the 386-MSCs underwent fragmentation before further evolution. The fragmentation processes were significantly impeded by the addition of extra indium myristate and accelerated by extra myristic acid, which is a fatty acid. The combined use of both resulted in InP branched nanostructures (BNSs), including nanorods, pods, hyper-branched NSs and dendrimer-like NSs. Before reaching such BNSs, 2 nm sized spherical NPs and 4 nm tetrahedral seeds appeared as intermediates. The fragmentation of 386-MSCs, which have a polytwistane crystal structure, resulted in the 2 nm sized spherical NPs, which are amorphous. In turn, the 2 nm NPs participated in the growth of BNSs, of which the final crystal structure is zinc blende. The amorphous 2 nm NPs are likely to be an intermediate in the crystal structure transformation to a phase that is more stable in bulk. In the syntheses of anisotropic NSs, structure-directing agents are commonly used, which typically bind selectively to particular crystal facets and promote anisotropic growth. Highly anisotropic InP structures, such as various BNSs, were obtained without using any structure-directing agents. This demonstrates that sophisticated control over the growth pathways using MSCs offers novel NSs that cannot be attained by conventional synthetic protocols.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...