Solution processed lead-free cesium titanium halide perovskites and their structural, thermal and optical characteristics
Abstract
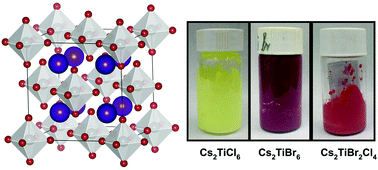
Metal halide based perovskite materials have attracted tremendous interest in optoelectronics. Although conventional lead (Pb) based organic/inorganic halide perovskites have been extensively studied and have realized highly efficient devices like solar cells and light emitting diodes, they are plagued with the toxicity of the Pb element, restraining their applications in environmentally and biologically friendly scenarios. Substitutes for Pb ions have been suggested, yet most of the Pb-free perovskites suffer from low stability and inferior efficiencies compared to their Pb based counterparts. In this work, we explore the synthesis of cesium titanium halide perovskites (Cs2TiX6, X = Cl, Br). At room-temperature, aqueous solution-based processes are developed to grow thermally stable, high quality Cs2Ti(BrxCl1−x)6 (0 < x < 1) crystals and films in large volume. Their structural, thermal and optical properties are systematically studied in experiments and compared with first principles calculations. The produced materials demonstrate a tunable, quasi-direct band gap from ∼1.7 eV to ∼2.5 eV and photoluminescence peaked from ∼535 nm to ∼670 nm. Furthermore, the materials are stable in an ambient environment up to ∼500 °C. These Pb-free perovskite materials will create opportunities for novel optical and electronic devices used in eco-friendly and bio-friendly environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...