Enhanced photovoltaic effect in Bi2FeMo0.7Ni0.3O6 ferroelectric thin films by tuning the thickness†
Abstract
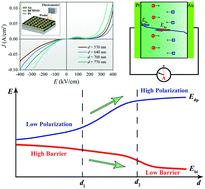
Ferroelectric photovoltaic (FE-PV) materials with excellent photocurrent output have stimulated many recent studies in solar energy material fields. How to improve the photocurrent by designing the structure of materials and devices through a simple approach is still a challenge. Here, enhanced photocurrent in Bi2FeMo0.7Ni0.3O6 (BFMNO) ferroelectric thin films is achieved by tuning the thickness of the thin films. With the increase of the thickness, the short circuit current increases first and then decreases. The maximum short circuit current reaches 0.09 mA cm−2 under 100 mW cm−2 when the thickness is 700 nm, which is nearly triple that of the thin film with the thickness of 570 nm. It is proposed that the compensation effect of the driving force comprising the depolarization field and build-in field is the main reason for the enhanced photocurrent. This work highlights a simple approach to enhance the photocurrent of FE-PV materials based on tuning of the thickness.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...