Recent research and development of local anesthetic-loaded microspheres
Abstract
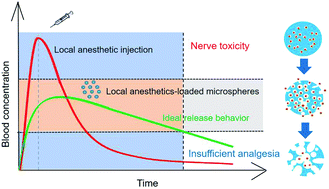
Local anesthetic drugs are widely used in postoperative analgesia, local nerve block in surgery, and in the therapy of chronic pain. Due to their short half-time, a single administration of local anesthetics merely maintains the nerve block for several hours, which cannot meet the long-term analgesia effect needed in clinical treatment. In order to break through this limitation of local anesthetics, research work regarding controlled drug release from microspheres has attracted broad and current interest. This review introduces the recent research and development in local anesthetic-loaded microspheres for future clinical applications, where for an efficient microsphere formulation, the most critical aspects are an optimum preparation method, a high loading efficiency, and an ideal release rate. This review first summarizes the recent preparation methods of local anesthetic-loaded microspheres, which includes emulsion-solvent evaporation, spray-drying, microfluidic droplets, and premix membrane emulsification technology. Next, strategies for increasing the loading efficiency of the drug in microspheres are reviewed based on the solidification conditions, polymer properties, microsphere formulation, including the external water phase, pH, and polymer concentration. Finally, the effects of the preparation conditions, material characteristics, particle characteristics, and hydrogel/microsphere composite systems on the controlled release behavior are summarized.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...